scipy.special.kolmogorov#
- scipy.special.kolmogorov(y, out=None) = <ufunc 'kolmogorov'>#
Kolmogorov 分佈的互補累積分布函數(生存函數)。
返回 Kolmogorov 極限分佈的互補累積分布函數(當 n 趨近於無限大時的
D_n*\sqrt(n)),用於檢驗經驗分布和理論分布之間是否相等的雙尾檢定。它等於(當 n->無限大時的極限)機率,即sqrt(n) * max absolute deviation > y。- 參數:
- y浮點數 陣列型
經驗累積分布函數 (ECDF) 和目標累積分布函數 (CDF) 之間的絕對偏差,乘以 sqrt(n)。
- outndarray,選填
用於函數結果的可選輸出陣列
- 回傳值:
- 純量或 ndarray
kolmogorov(y) 的值
另請參閱
kolmogi分佈的反生存函數
scipy.stats.kstwobign以連續分佈的形式提供功能
smirnov,smirnovi用於單尾分佈的函數
註解
kolmogorov被 stats.kstest 用於 Kolmogorov-Smirnov 適合度檢定。基於歷史原因,此函數在 scpy.special 中公開,但要獲得最準確的 CDF/SF/PDF/PPF/ISF 計算,建議使用 stats.kstwobign 分佈。範例
顯示間隙至少為 0、0.5 和 1.0 的機率。
>>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy.special import kolmogorov >>> from scipy.stats import kstwobign >>> kolmogorov([0, 0.5, 1.0]) array([ 1. , 0.96394524, 0.26999967])
將從 Laplace(0, 1) 分佈中抽取的 1000 個樣本與目標分佈 Normal(0, 1) 分佈進行比較。
>>> from scipy.stats import norm, laplace >>> rng = np.random.default_rng() >>> n = 1000 >>> lap01 = laplace(0, 1) >>> x = np.sort(lap01.rvs(n, random_state=rng)) >>> np.mean(x), np.std(x) (-0.05841730131499543, 1.3968109101997568)
建構經驗累積分布函數 (Empirical CDF) 和 K-S 統計量 Dn。
>>> target = norm(0,1) # Normal mean 0, stddev 1 >>> cdfs = target.cdf(x) >>> ecdfs = np.arange(n+1, dtype=float)/n >>> gaps = np.column_stack([cdfs - ecdfs[:n], ecdfs[1:] - cdfs]) >>> Dn = np.max(gaps) >>> Kn = np.sqrt(n) * Dn >>> print('Dn=%f, sqrt(n)*Dn=%f' % (Dn, Kn)) Dn=0.043363, sqrt(n)*Dn=1.371265 >>> print(chr(10).join(['For a sample of size n drawn from a N(0, 1) distribution:', ... ' the approximate Kolmogorov probability that sqrt(n)*Dn>=%f is %f' % ... (Kn, kolmogorov(Kn)), ... ' the approximate Kolmogorov probability that sqrt(n)*Dn<=%f is %f' % ... (Kn, kstwobign.cdf(Kn))])) For a sample of size n drawn from a N(0, 1) distribution: the approximate Kolmogorov probability that sqrt(n)*Dn>=1.371265 is 0.046533 the approximate Kolmogorov probability that sqrt(n)*Dn<=1.371265 is 0.953467
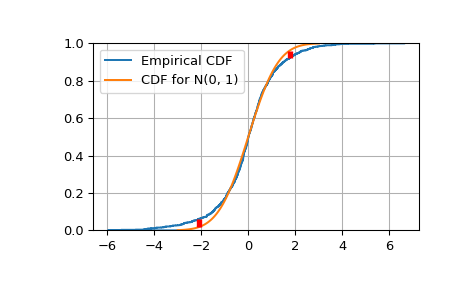
繪製經驗累積分布函數 (Empirical CDF) 對目標 N(0, 1) 累積分布函數 (CDF) 的圖。
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> plt.step(np.concatenate([[-3], x]), ecdfs, where='post', label='Empirical CDF') >>> x3 = np.linspace(-3, 3, 100) >>> plt.plot(x3, target.cdf(x3), label='CDF for N(0, 1)') >>> plt.ylim([0, 1]); plt.grid(True); plt.legend(); >>> # Add vertical lines marking Dn+ and Dn- >>> iminus, iplus = np.argmax(gaps, axis=0) >>> plt.vlines([x[iminus]], ecdfs[iminus], cdfs[iminus], ... color='r', linestyle='dashed', lw=4) >>> plt.vlines([x[iplus]], cdfs[iplus], ecdfs[iplus+1], ... color='r', linestyle='dashed', lw=4) >>> plt.show()