scipy.signal.
correlate2d#
- scipy.signal.correlate2d(in1, in2, mode='full', boundary='fill', fillvalue=0)[原始碼]#
對兩個 2 維陣列進行互相關運算。
對 in1 和 in2 進行互相關運算,輸出大小由 mode 決定,邊界條件由 boundary 和 fillvalue 決定。
- 參數:
- in1array_like
第一個輸入。
- in2array_like
第二個輸入。應具有與 in1 相同的維度數。
- modestr {‘full’, ‘valid’, ‘same’}, optional
指示輸出大小的字串
full輸出是輸入的完整離散線性互相關。(預設)
valid輸出僅包含不依賴零填充的元素。在 ‘valid’ 模式下,in1 或 in2 在每個維度上都必須至少與另一個一樣大。
same輸出與 in1 大小相同,相對於 ‘full’ 輸出居中。
- boundarystr {‘fill’, ‘wrap’, ‘symm’}, optional
指示如何處理邊界的旗標
fill用 fillvalue 填充輸入陣列。(預設)
wrap循環邊界條件。
symm對稱邊界條件。
- fillvaluescalar, optional
用於填充輸入陣列的值。預設值為 0。
- 返回:
- correlate2dndarray
一個 2 維陣列,包含 in1 與 in2 的離散線性互相關的子集。
註解
當對偶數長度的輸入使用 “same” 模式時,
correlate和correlate2d的輸出會有所不同:它們之間存在 1 個索引的偏移。範例
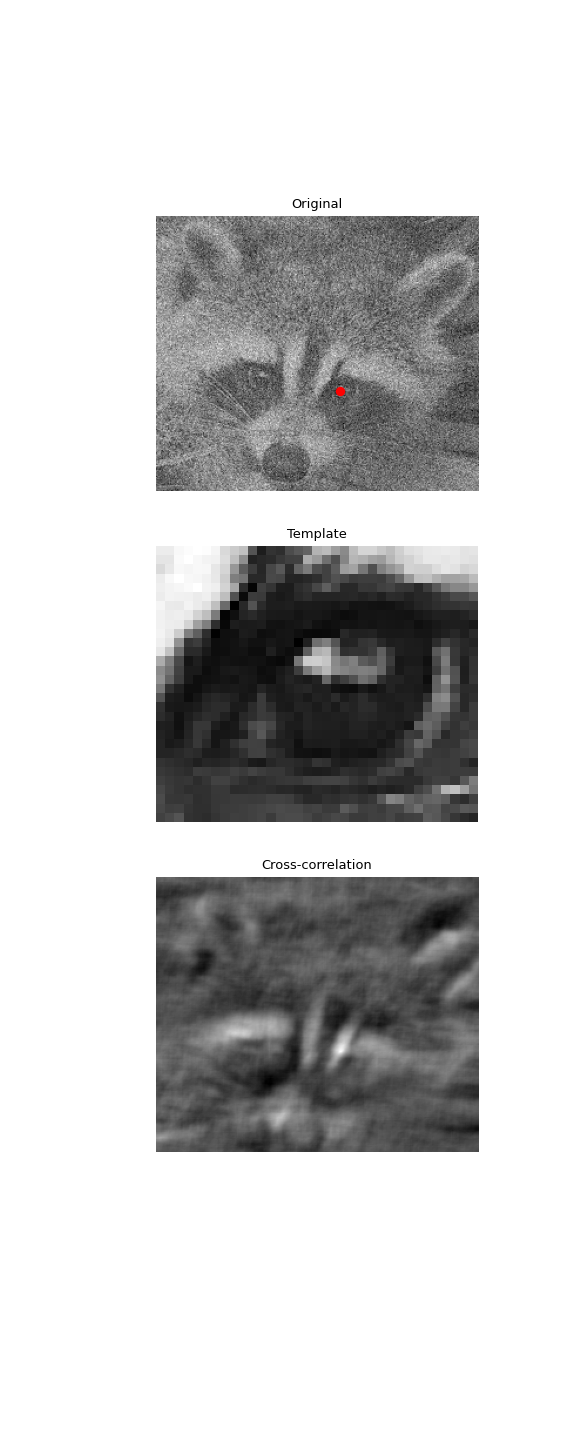
使用 2D 互相關來尋找雜訊影像中範本的位置
>>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy import signal, datasets, ndimage >>> rng = np.random.default_rng() >>> face = datasets.face(gray=True) - datasets.face(gray=True).mean() >>> face = ndimage.zoom(face[30:500, 400:950], 0.5) # extract the face >>> template = np.copy(face[135:165, 140:175]) # right eye >>> template -= template.mean() >>> face = face + rng.standard_normal(face.shape) * 50 # add noise >>> corr = signal.correlate2d(face, template, boundary='symm', mode='same') >>> y, x = np.unravel_index(np.argmax(corr), corr.shape) # find the match
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> fig, (ax_orig, ax_template, ax_corr) = plt.subplots(3, 1, ... figsize=(6, 15)) >>> ax_orig.imshow(face, cmap='gray') >>> ax_orig.set_title('Original') >>> ax_orig.set_axis_off() >>> ax_template.imshow(template, cmap='gray') >>> ax_template.set_title('Template') >>> ax_template.set_axis_off() >>> ax_corr.imshow(corr, cmap='gray') >>> ax_corr.set_title('Cross-correlation') >>> ax_corr.set_axis_off() >>> ax_orig.plot(x, y, 'ro') >>> fig.show()