convolve#
- scipy.signal.convolve(in1, in2, mode='full', method='auto')[source]#
對兩個 N 維陣列進行卷積運算。
對 in1 和 in2 進行卷積運算,輸出大小由 mode 參數決定。
- 參數:
- in1array_like
第一個輸入。
- in2array_like
第二個輸入。應與 in1 具有相同的維度數量。
- modestr {‘full’, ‘valid’, ‘same’}, 選項性
一個字串,指示輸出的尺寸
full輸出是輸入的完整離散線性卷積。(預設)
valid輸出僅包含不依賴零填充的元素。在 ‘valid’ 模式中,in1 或 in2 必須在每個維度上至少與另一個一樣大。
same輸出與 in1 的大小相同,相對於 'full' 輸出居中。
- methodstr {‘auto’, ‘direct’, ‘fft’}, 選項性
一個字串,指示用於計算卷積的方法。
direct卷積直接從總和(卷積的定義)確定。
fft傅立葉轉換用於通過呼叫
fftconvolve來執行卷積。auto根據對哪個方法更快的估計值自動選擇直接或傅立葉方法(預設)。請參閱「Notes」以了解更多詳細資訊。
在版本 0.19.0 中新增。
- 回傳:
- convolvearray
一個 N 維陣列,包含 in1 與 in2 的離散線性卷積的子集。
- 警告:
- RuntimeWarning
在包含 NAN 或 INF 的輸入上使用 FFT 卷積將導致整個輸出為 NAN 或 INF。當您的輸入包含 NAN 或 INF 值時,請使用 method='direct'。
另請參閱
numpy.polymul執行多項式乘法(相同的操作,但也接受 poly1d 物件)
choose_conv_method選擇最快的適當卷積方法
fftconvolve始終使用 FFT 方法。
oaconvolve使用重疊相加法進行卷積,當輸入陣列很大且尺寸差異顯著時,通常更快。
註解
預設情況下,
convolve和correlate使用method='auto',它會呼叫choose_conv_method來使用預先計算的值選擇最快的方法 (choose_conv_method也可以使用關鍵字引數測量真實世界的計時)。由於fftconvolve依賴浮點數,因此存在某些約束可能會強制使用method='direct'(更多詳細資訊請參閱choose_conv_method文件字串)。範例
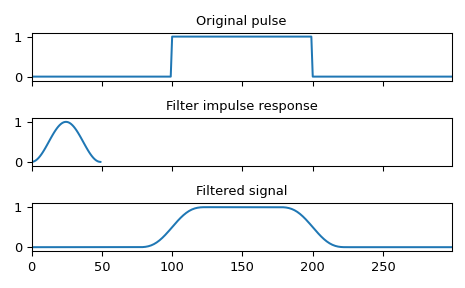
使用 Hann 視窗平滑方形脈衝
>>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy import signal >>> sig = np.repeat([0., 1., 0.], 100) >>> win = signal.windows.hann(50) >>> filtered = signal.convolve(sig, win, mode='same') / sum(win)
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> fig, (ax_orig, ax_win, ax_filt) = plt.subplots(3, 1, sharex=True) >>> ax_orig.plot(sig) >>> ax_orig.set_title('Original pulse') >>> ax_orig.margins(0, 0.1) >>> ax_win.plot(win) >>> ax_win.set_title('Filter impulse response') >>> ax_win.margins(0, 0.1) >>> ax_filt.plot(filtered) >>> ax_filt.set_title('Filtered signal') >>> ax_filt.margins(0, 0.1) >>> fig.tight_layout() >>> fig.show()