HalfspaceIntersection#
- class scipy.spatial.HalfspaceIntersection(halfspaces, interior_point, incremental=False, qhull_options=None)#
N 維空間中的半空間交集。
在 0.19.0 版本中加入。
- 參數:
- halfspacesndarray of floats, shape (nineq, ndim+1)
格式為 [A; b] 的 Ax + b <= 0 形式的堆疊不等式
- interior_pointndarray of floats, shape (ndim,)
明顯位於半空間定義區域內部的點。也稱為可行點,可以透過線性規劃獲得。
- incrementalbool, optional
允許增量新增半空間。這會佔用一些額外資源。
- qhull_optionsstr, optional
傳遞給 Qhull 的額外選項。詳情請參閱 Qhull 手冊。(預設值:ndim > 4 時為 “Qx”,否則為 “”)選項 “H” 始終啟用。
- 引發:
- QhullError
當 Qhull 遇到錯誤情況時引發,例如未啟用解決選項時的幾何退化。
- ValueError
如果給定的輸入陣列不相容則引發。
註解
交集是使用 Qhull 函式庫 計算的。這重現了 Qhull 的 “qhalf” 功能。
參考文獻
[Qhull][1]S. Boyd, L. Vandenberghe, Convex Optimization,可於 http://stanford.edu/~boyd/cvxbook/ 取得
範例
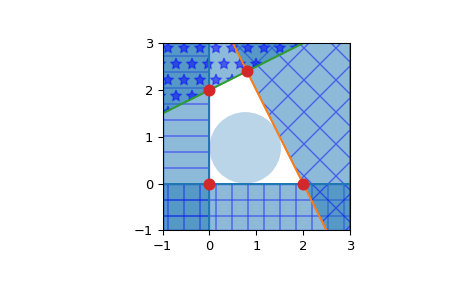
形成某些多邊形的平面的半空間交集
>>> from scipy.spatial import HalfspaceIntersection >>> import numpy as np >>> halfspaces = np.array([[-1, 0., 0.], ... [0., -1., 0.], ... [2., 1., -4.], ... [-0.5, 1., -2.]]) >>> feasible_point = np.array([0.5, 0.5]) >>> hs = HalfspaceIntersection(halfspaces, feasible_point)
繪製半空間為填充區域和交點
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> fig = plt.figure() >>> ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1, aspect='equal') >>> xlim, ylim = (-1, 3), (-1, 3) >>> ax.set_xlim(xlim) >>> ax.set_ylim(ylim) >>> x = np.linspace(-1, 3, 100) >>> symbols = ['-', '+', 'x', '*'] >>> signs = [0, 0, -1, -1] >>> fmt = {"color": None, "edgecolor": "b", "alpha": 0.5} >>> for h, sym, sign in zip(halfspaces, symbols, signs): ... hlist = h.tolist() ... fmt["hatch"] = sym ... if h[1]== 0: ... ax.axvline(-h[2]/h[0], label='{}x+{}y+{}=0'.format(*hlist)) ... xi = np.linspace(xlim[sign], -h[2]/h[0], 100) ... ax.fill_between(xi, ylim[0], ylim[1], **fmt) ... else: ... ax.plot(x, (-h[2]-h[0]*x)/h[1], label='{}x+{}y+{}=0'.format(*hlist)) ... ax.fill_between(x, (-h[2]-h[0]*x)/h[1], ylim[sign], **fmt) >>> x, y = zip(*hs.intersections) >>> ax.plot(x, y, 'o', markersize=8)
預設情況下,qhull 不提供計算內部點的方法。這可以使用線性規劃輕鬆計算。考慮 \(Ax + b \leq 0\) 形式的半空間,求解線性規劃
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}max \: y\\s.t. Ax + y ||A_i|| \leq -b\end{aligned}\end{align} \]其中 \(A_i\) 是 A 的列,即每個平面的法向量。
將產生一個點 x,該點 x 是凸多面體內最遠的點。準確來說,它是內切於多面體的最大超球體的中心,半徑為 y。此點稱為多面體的 Chebyshev 中心(參見 [1] 4.3.1, pp148-149)。Qhull 輸出的方程式始終是標準化的。
>>> from scipy.optimize import linprog >>> from matplotlib.patches import Circle >>> norm_vector = np.reshape(np.linalg.norm(halfspaces[:, :-1], axis=1), ... (halfspaces.shape[0], 1)) >>> c = np.zeros((halfspaces.shape[1],)) >>> c[-1] = -1 >>> A = np.hstack((halfspaces[:, :-1], norm_vector)) >>> b = - halfspaces[:, -1:] >>> res = linprog(c, A_ub=A, b_ub=b, bounds=(None, None)) >>> x = res.x[:-1] >>> y = res.x[-1] >>> circle = Circle(x, radius=y, alpha=0.3) >>> ax.add_patch(circle) >>> plt.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.6, 1.0)) >>> plt.show()
- 屬性:
- halfspacesndarray of double, shape (nineq, ndim+1)
輸入半空間。
- interior_point :ndarray of floats, shape (ndim,)
輸入內部點。
- intersectionsndarray of double, shape (ninter, ndim)
所有半空間的交集。
- dual_pointsndarray of double, shape (nineq, ndim)
輸入半空間的對偶點。
- dual_facetslist of lists of ints
形成對偶凸包(不一定是單純形)面的點的索引。
- dual_verticesndarray of ints, shape (nvertices,)
形成對偶凸包頂點的半空間索引。對於 2-D 凸包,頂點以逆時針順序排列。對於其他維度,它們以輸入順序排列。
- dual_equationsndarray of double, shape (nfacet, ndim+1)
[法向量, 偏移量] 形成對偶面的超平面方程式(更多資訊請參閱 Qhull 文件)。
- dual_areafloat
對偶凸包的面積
- dual_volumefloat
對偶凸包的體積
方法
add_halfspaces(halfspaces[, restart])處理一組額外的新半空間。
close()完成增量處理。