scipy.signal.ShortTimeFFT.
頻譜圖#
- ShortTimeFFT.spectrogram(x, y=None, detr=None, *, p0=None, p1=None, k_offset=0, padding='zeros', axis=-1)[source]#
計算頻譜圖或交叉頻譜圖。
頻譜圖是 STFT 的絕對值平方,亦即對於給定的
S[q,p],其值為abs(S[q,p])**2,因此始終為非負值。對於兩個 STFTSx[q,p]、Sy[q,p],交叉頻譜圖定義為Sx[q,p] * np.conj(Sy[q,p]),且為複數值。這是一個方便的函式,用於呼叫stft/stft_detrend,因此所有參數都在那裡討論。如果 y 不是None,則它需要與 x 具有相同的形狀。另請參閱
stft執行短時傅立葉轉換。
stft_detrendSTFT,從每個區段中減去趨勢。
scipy.signal.ShortTimeFFT此方法所屬的類別。
範例
以下範例顯示一個頻率變化的方波頻譜圖 \(f_i(t)\) (在圖中以綠色虛線標記),以 20 Hz 採樣
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy.signal import square, ShortTimeFFT >>> from scipy.signal.windows import gaussian ... >>> T_x, N = 1 / 20, 1000 # 20 Hz sampling rate for 50 s signal >>> t_x = np.arange(N) * T_x # time indexes for signal >>> f_i = 5e-3*(t_x - t_x[N // 3])**2 + 1 # varying frequency >>> x = square(2*np.pi*np.cumsum(f_i)*T_x) # the signal
使用的 Gaussian 視窗為 50 個樣本或 2.5 秒長。參數
mfft=800(過採樣因子 16) 和hop間隔 2 在ShortTimeFFT中被選擇來產生足夠的點數>>> g_std = 12 # standard deviation for Gaussian window in samples >>> win = gaussian(50, std=g_std, sym=True) # symmetric Gaussian wind. >>> SFT = ShortTimeFFT(win, hop=2, fs=1/T_x, mfft=800, scale_to='psd') >>> Sx2 = SFT.spectrogram(x) # calculate absolute square of STFT
圖表的色圖以對數方式縮放,因為功率譜密度以 dB 為單位。訊號 x 的時間範圍以垂直虛線標記,陰影區域標記邊界效應的存在
>>> fig1, ax1 = plt.subplots(figsize=(6., 4.)) # enlarge plot a bit >>> t_lo, t_hi = SFT.extent(N)[:2] # time range of plot >>> ax1.set_title(rf"Spectrogram ({SFT.m_num*SFT.T:g}$\,s$ Gaussian " + ... rf"window, $\sigma_t={g_std*SFT.T:g}\,$s)") >>> ax1.set(xlabel=f"Time $t$ in seconds ({SFT.p_num(N)} slices, " + ... rf"$\Delta t = {SFT.delta_t:g}\,$s)", ... ylabel=f"Freq. $f$ in Hz ({SFT.f_pts} bins, " + ... rf"$\Delta f = {SFT.delta_f:g}\,$Hz)", ... xlim=(t_lo, t_hi)) >>> Sx_dB = 10 * np.log10(np.fmax(Sx2, 1e-4)) # limit range to -40 dB >>> im1 = ax1.imshow(Sx_dB, origin='lower', aspect='auto', ... extent=SFT.extent(N), cmap='magma') >>> ax1.plot(t_x, f_i, 'g--', alpha=.5, label='$f_i(t)$') >>> fig1.colorbar(im1, label='Power Spectral Density ' + ... r"$20\,\log_{10}|S_x(t, f)|$ in dB") ... >>> # Shade areas where window slices stick out to the side: >>> for t0_, t1_ in [(t_lo, SFT.lower_border_end[0] * SFT.T), ... (SFT.upper_border_begin(N)[0] * SFT.T, t_hi)]: ... ax1.axvspan(t0_, t1_, color='w', linewidth=0, alpha=.3) >>> for t_ in [0, N * SFT.T]: # mark signal borders with vertical line ... ax1.axvline(t_, color='c', linestyle='--', alpha=0.5) >>> ax1.legend() >>> fig1.tight_layout() >>> plt.show()
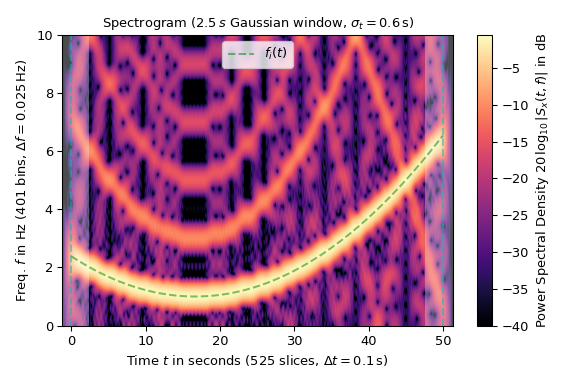
對數縮放揭示了方波的奇次諧波,這些諧波在 10 Hz 的奈奎斯特頻率處被反射。這種混疊也是圖中雜訊偽影的主要來源。