scipy.ndimage.
sobel#
- scipy.ndimage.sobel(input, axis=-1, output=None, mode='reflect', cval=0.0)[原始碼]#
計算 Sobel 濾波器。
- 參數:
- inputarray_like
輸入陣列。
- axisint,選用
要沿其計算的 input 軸。預設值為 -1。
- outputarray 或 dtype,選用
放置輸出的陣列,或傳回陣列的 dtype。預設會建立與輸入相同 dtype 的陣列。
- modestr 或 sequence,選用
mode 參數決定當濾波器與邊界重疊時,輸入陣列的擴展方式。透過傳遞模式序列,其長度等於輸入陣列的維度數,可以沿每個軸指定不同的模式。預設值為 ‘reflect’。有效值及其行為如下
- ‘reflect’ (d c b a | a b c d | d c b a)
輸入會透過反射最後一個像素的邊緣來擴展。此模式有時也稱為半樣本對稱。
- ‘constant’ (k k k k | a b c d | k k k k)
輸入會透過以相同的常數值填充邊緣以外的所有值來擴展,常數值由 cval 參數定義。
- ‘nearest’ (a a a a | a b c d | d d d d)
輸入會透過複製最後一個像素來擴展。
- ‘mirror’ (d c b | a b c d | c b a)
輸入會透過反射最後一個像素的中心來擴展。此模式有時也稱為全樣本對稱。
- ‘wrap’ (a b c d | a b c d | a b c d)
輸入會透過環繞到相反的邊緣來擴展。
為了與內插函數保持一致,也可以使用以下模式名稱
- ‘grid-constant’
這是 ‘constant’ 的同義詞。
- ‘grid-mirror’
這是 ‘reflect’ 的同義詞。
- ‘grid-wrap’
這是 ‘wrap’ 的同義詞。
- cval純量,選用
如果 mode 為 ‘constant’,則填充輸入邊緣之外的值。預設值為 0.0。
- 傳回值:
- sobelndarray
已濾波的陣列。具有與 input 相同的形狀。
註解
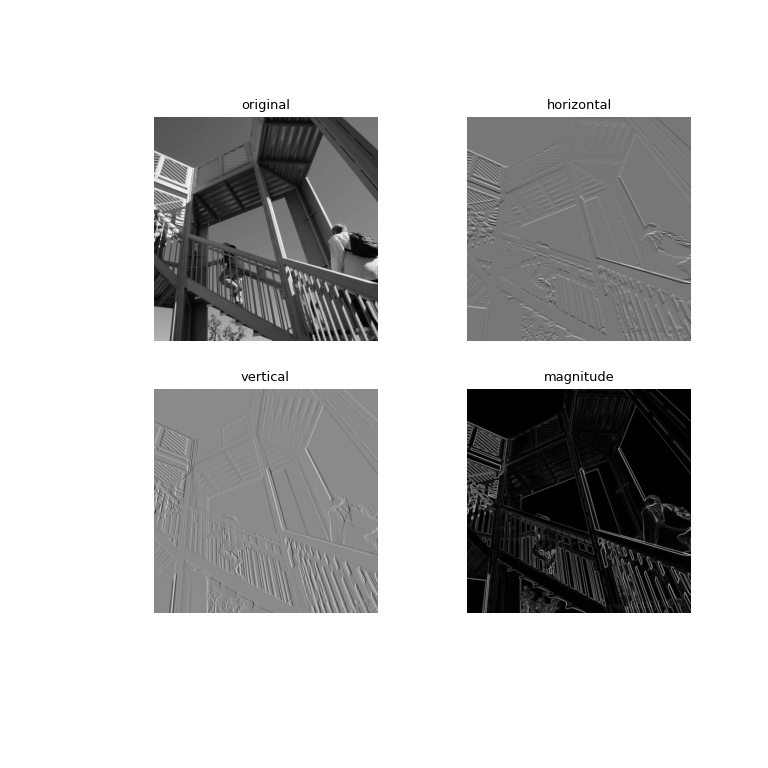
此函數計算軸特定的 Sobel 梯度。水平邊緣可以使用水平變換 (axis=0) 強調,垂直邊緣可以使用垂直變換 (axis=1) 強調,依此類推,適用於更高維度。這些可以組合起來以提供幅度。
範例
>>> from scipy import ndimage, datasets >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> import numpy as np >>> ascent = datasets.ascent().astype('int32') >>> sobel_h = ndimage.sobel(ascent, 0) # horizontal gradient >>> sobel_v = ndimage.sobel(ascent, 1) # vertical gradient >>> magnitude = np.sqrt(sobel_h**2 + sobel_v**2) >>> magnitude *= 255.0 / np.max(magnitude) # normalization >>> fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(8, 8)) >>> plt.gray() # show the filtered result in grayscale >>> axs[0, 0].imshow(ascent) >>> axs[0, 1].imshow(sobel_h) >>> axs[1, 0].imshow(sobel_v) >>> axs[1, 1].imshow(magnitude) >>> titles = ["original", "horizontal", "vertical", "magnitude"] >>> for i, ax in enumerate(axs.ravel()): ... ax.set_title(titles[i]) ... ax.axis("off") >>> plt.show()