scipy.interpolate.
approximate_taylor_polynomial#
- scipy.interpolate.approximate_taylor_polynomial(f, x, degree, scale, order=None)[source]#
通過多項式擬合估計 f 在 x 處的泰勒多項式。
- 參數:
- f可呼叫物件 (callable)
尋找泰勒多項式的函數。 應接受 x 值的向量。
- x純量
要評估多項式的點。
- degree整數
泰勒多項式的次數
- scale純量
用於評估泰勒多項式的區間寬度。 此寬度範圍內擴展的函數值用於擬合多項式。 必須仔細選擇。
- order整數或 None,可選
用於擬合的多項式階數; f 將被評估
order+1次。 如果為 None,則使用 degree。
- 返回值:
- ppoly1d 實例
泰勒多項式(已轉換到原點,因此例如 p(0)=f(x))。
筆記
“scale” 的適當選擇是一種權衡; 太大會導致函數與其泰勒多項式相差太大而無法獲得好的答案,太小則捨入誤差會淹沒高階項。 即使在理想情況下,所使用的演算法在 30 階左右也會變得數值不穩定。
選擇略大於 degree 的 order 可能會改善高階項。
範例
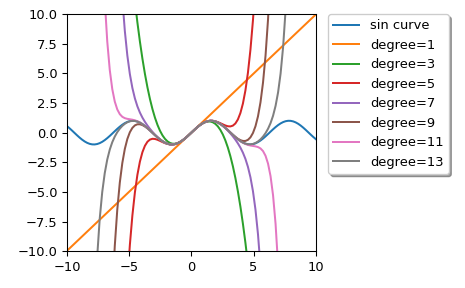
我們可以使用各種次數計算 sin 函數的泰勒近似多項式
>>> import numpy as np >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> from scipy.interpolate import approximate_taylor_polynomial >>> x = np.linspace(-10.0, 10.0, num=100) >>> plt.plot(x, np.sin(x), label="sin curve") >>> for degree in np.arange(1, 15, step=2): ... sin_taylor = approximate_taylor_polynomial(np.sin, 0, degree, 1, ... order=degree + 2) ... plt.plot(x, sin_taylor(x), label=f"degree={degree}") >>> plt.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.05, 1), loc='upper left', ... borderaxespad=0.0, shadow=True) >>> plt.tight_layout() >>> plt.axis([-10, 10, -10, 10]) >>> plt.show()