Rotation#
- class scipy.spatial.transform.Rotation#
3 維旋轉。
此類別提供介面,可從下列項目初始化和表示旋轉:
四元數
旋轉矩陣
旋轉向量
修正羅德里格參數
歐拉角
支援對旋轉進行以下操作:
應用於向量
旋轉合成
旋轉反轉
旋轉索引
由於單一
Rotation實例中可以儲存多個旋轉變換,因此支援旋轉內的索引。若要建立
Rotation物件,請使用from_...方法(請參閱以下範例)。Rotation(...)不應直接實例化。另請參閱
註解
在 1.2.0 版本中新增。
範例
>>> from scipy.spatial.transform import Rotation as R >>> import numpy as np
Rotation實例可以使用上述任何格式初始化,並轉換為任何其他格式。底層物件與用於初始化的表示形式無關。考慮繞 z 軸逆時針旋轉 90 度。這對應於以下四元數(純量最後格式):
>>> r = R.from_quat([0, 0, np.sin(np.pi/4), np.cos(np.pi/4)])
旋轉可以用任何其他格式表示
>>> r.as_matrix() array([[ 2.22044605e-16, -1.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00], [ 1.00000000e+00, 2.22044605e-16, 0.00000000e+00], [ 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 1.00000000e+00]]) >>> r.as_rotvec() array([0. , 0. , 1.57079633]) >>> r.as_euler('zyx', degrees=True) array([90., 0., 0.])
相同的旋轉可以使用旋轉矩陣初始化
>>> r = R.from_matrix([[0, -1, 0], ... [1, 0, 0], ... [0, 0, 1]])
以其他格式表示
>>> r.as_quat() array([0. , 0. , 0.70710678, 0.70710678]) >>> r.as_rotvec() array([0. , 0. , 1.57079633]) >>> r.as_euler('zyx', degrees=True) array([90., 0., 0.])
對應於此旋轉的旋轉向量由下式給出
>>> r = R.from_rotvec(np.pi/2 * np.array([0, 0, 1]))
以其他格式表示
>>> r.as_quat() array([0. , 0. , 0.70710678, 0.70710678]) >>> r.as_matrix() array([[ 2.22044605e-16, -1.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00], [ 1.00000000e+00, 2.22044605e-16, 0.00000000e+00], [ 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 1.00000000e+00]]) >>> r.as_euler('zyx', degrees=True) array([90., 0., 0.])
from_euler方法在其支援的輸入格式範圍內非常靈活。在這裡,我們初始化一個繞單一軸的單一旋轉>>> r = R.from_euler('z', 90, degrees=True)
同樣,物件與表示形式無關,並且可以轉換為任何其他格式
>>> r.as_quat() array([0. , 0. , 0.70710678, 0.70710678]) >>> r.as_matrix() array([[ 2.22044605e-16, -1.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00], [ 1.00000000e+00, 2.22044605e-16, 0.00000000e+00], [ 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 1.00000000e+00]]) >>> r.as_rotvec() array([0. , 0. , 1.57079633])
也可以使用任何
from_...函數在單一實例中初始化多個旋轉。在這裡,我們使用from_euler方法初始化 3 個旋轉的堆疊>>> r = R.from_euler('zyx', [ ... [90, 0, 0], ... [0, 45, 0], ... [45, 60, 30]], degrees=True)
其他表示形式現在也傳回 3 個旋轉的堆疊。例如
>>> r.as_quat() array([[0. , 0. , 0.70710678, 0.70710678], [0. , 0.38268343, 0. , 0.92387953], [0.39190384, 0.36042341, 0.43967974, 0.72331741]])
將上述旋轉應用到向量上
>>> v = [1, 2, 3] >>> r.apply(v) array([[-2. , 1. , 3. ], [ 2.82842712, 2. , 1.41421356], [ 2.24452282, 0.78093109, 2.89002836]])
Rotation實例可以像單一 1D 陣列或列表一樣進行索引和切片>>> r.as_quat() array([[0. , 0. , 0.70710678, 0.70710678], [0. , 0.38268343, 0. , 0.92387953], [0.39190384, 0.36042341, 0.43967974, 0.72331741]]) >>> p = r[0] >>> p.as_matrix() array([[ 2.22044605e-16, -1.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00], [ 1.00000000e+00, 2.22044605e-16, 0.00000000e+00], [ 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 1.00000000e+00]]) >>> q = r[1:3] >>> q.as_quat() array([[0. , 0.38268343, 0. , 0.92387953], [0.39190384, 0.36042341, 0.43967974, 0.72331741]])
事實上,它可以轉換為 numpy.array
>>> r_array = np.asarray(r) >>> r_array.shape (3,) >>> r_array[0].as_matrix() array([[ 2.22044605e-16, -1.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00], [ 1.00000000e+00, 2.22044605e-16, 0.00000000e+00], [ 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 1.00000000e+00]])
可以使用
*運算子組合多個旋轉>>> r1 = R.from_euler('z', 90, degrees=True) >>> r2 = R.from_rotvec([np.pi/4, 0, 0]) >>> v = [1, 2, 3] >>> r2.apply(r1.apply(v)) array([-2. , -1.41421356, 2.82842712]) >>> r3 = r2 * r1 # Note the order >>> r3.apply(v) array([-2. , -1.41421356, 2.82842712])
可以使用
**運算子將旋轉與自身組合>>> p = R.from_rotvec([1, 0, 0]) >>> q = p ** 2 >>> q.as_rotvec() array([2., 0., 0.])
最後,也可以反轉旋轉
>>> r1 = R.from_euler('z', [90, 45], degrees=True) >>> r2 = r1.inv() >>> r2.as_euler('zyx', degrees=True) array([[-90., 0., 0.], [-45., 0., 0.]])
以下函數可用於使用 Matplotlib 繪製旋轉,方法是顯示它們如何變換標準 x、y、z 座標軸
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> def plot_rotated_axes(ax, r, name=None, offset=(0, 0, 0), scale=1): ... colors = ("#FF6666", "#005533", "#1199EE") # Colorblind-safe RGB ... loc = np.array([offset, offset]) ... for i, (axis, c) in enumerate(zip((ax.xaxis, ax.yaxis, ax.zaxis), ... colors)): ... axlabel = axis.axis_name ... axis.set_label_text(axlabel) ... axis.label.set_color(c) ... axis.line.set_color(c) ... axis.set_tick_params(colors=c) ... line = np.zeros((2, 3)) ... line[1, i] = scale ... line_rot = r.apply(line) ... line_plot = line_rot + loc ... ax.plot(line_plot[:, 0], line_plot[:, 1], line_plot[:, 2], c) ... text_loc = line[1]*1.2 ... text_loc_rot = r.apply(text_loc) ... text_plot = text_loc_rot + loc[0] ... ax.text(*text_plot, axlabel.upper(), color=c, ... va="center", ha="center") ... ax.text(*offset, name, color="k", va="center", ha="center", ... bbox={"fc": "w", "alpha": 0.8, "boxstyle": "circle"})
建立三個旋轉 - 單位旋轉以及使用內在和外在約定的兩個歐拉旋轉
>>> r0 = R.identity() >>> r1 = R.from_euler("ZYX", [90, -30, 0], degrees=True) # intrinsic >>> r2 = R.from_euler("zyx", [90, -30, 0], degrees=True) # extrinsic
將所有三個旋轉新增到單一繪圖中
>>> ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(projection="3d", proj_type="ortho") >>> plot_rotated_axes(ax, r0, name="r0", offset=(0, 0, 0)) >>> plot_rotated_axes(ax, r1, name="r1", offset=(3, 0, 0)) >>> plot_rotated_axes(ax, r2, name="r2", offset=(6, 0, 0)) >>> _ = ax.annotate( ... "r0: Identity Rotation\n" ... "r1: Intrinsic Euler Rotation (ZYX)\n" ... "r2: Extrinsic Euler Rotation (zyx)", ... xy=(0.6, 0.7), xycoords="axes fraction", ha="left" ... ) >>> ax.set(xlim=(-1.25, 7.25), ylim=(-1.25, 1.25), zlim=(-1.25, 1.25)) >>> ax.set(xticks=range(-1, 8), yticks=[-1, 0, 1], zticks=[-1, 0, 1]) >>> ax.set_aspect("equal", adjustable="box") >>> ax.figure.set_size_inches(6, 5) >>> plt.tight_layout()
顯示繪圖
>>> plt.show()
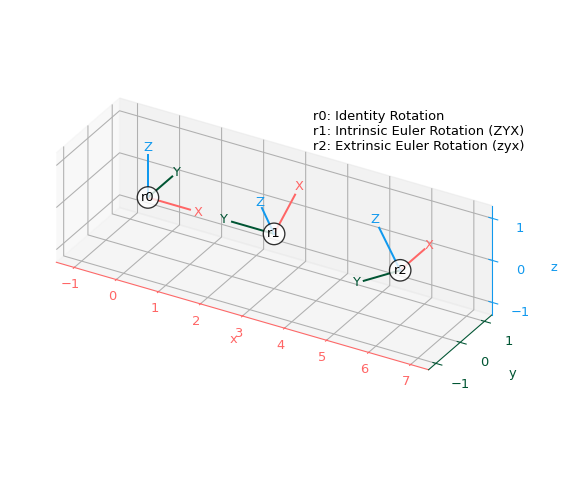
這些範例作為
Rotation類別的概觀,並重點介紹主要功能。如需支援的輸入和輸出格式範圍的更完整範例,請參閱個別方法的範例。- 屬性:
single此實例是否表示單一旋轉。
方法
此物件中包含的旋轉次數。
from_quat(cls, quat, *[, scalar_first])從四元數初始化。
from_matrix(cls, matrix)從旋轉矩陣初始化。
from_rotvec(cls, rotvec[, degrees])從旋轉向量初始化。
from_mrp(cls, mrp)從修正羅德里格參數 (MRP) 初始化。
from_euler(cls, seq, angles[, degrees])從歐拉角初始化。
from_davenport(cls, axes, order, angles[, ...])從 Davenport 角初始化。
as_quat(self[, canonical, scalar_first])表示為四元數。
as_matrix(self)表示為旋轉矩陣。
as_rotvec(self[, degrees])表示為旋轉向量。
as_mrp(self)表示為修正羅德里格參數 (MRP)。
as_euler(self, seq[, degrees])表示為歐拉角。
as_davenport(self, axes, order[, degrees])表示為 Davenport 角。
concatenate(cls, rotations)將
Rotation物件序列串連成單一物件。apply(self, vectors[, inverse])將此旋轉應用於一組向量。
將此旋轉與另一個旋轉合成。
將此旋轉與自身合成 n 次。
inv(self)反轉此旋轉。
magnitude(self)取得旋轉的量值。
approx_equal(self, Rotation other[, atol, ...])判斷另一個旋轉是否與此旋轉近似相等。
mean(self[, weights])取得旋轉的平均值。
reduce(self[, left, right, return_indices])使用提供的旋轉群組減少此旋轉。
create_group(cls, group[, axis])建立 3D 旋轉群組。
從物件中提取給定索引處的旋轉。
identity(cls[, num])取得單位旋轉。
random(cls[, num, rng])產生均勻分佈的旋轉。
align_vectors(cls, a, b[, weights, ...])估計最佳對齊兩組向量的旋轉。