dpss#
- scipy.signal.windows.dpss(M, NW, Kmax=None, sym=True, norm=None, return_ratios=False)[原始碼]#
計算離散長球面序列 (DPSS)。
DPSS(或 Slepian 序列)常用於多錐度功率譜密度估計(請參閱 [1])。序列中的第一個視窗可用於最大化主瓣中的能量集中度,也稱為 Slepian 視窗。
- 參數:
- Mint
視窗長度。
- NWfloat
標準化半頻寬,對應於
2*NW = BW/f0 = BW*M*dt,其中dt視為 1。- Kmaxint | None, optional
要傳回的 DPSS 視窗數量(階數
0到Kmax-1)。如果為 None(預設值),則僅傳回形狀為(M,)的單個視窗,而不是形狀為(Kmax, M)的視窗陣列。- symbool, optional
當 True(預設值)時,產生對稱視窗,用於濾波器設計。當 False 時,產生週期性視窗,用於頻譜分析。
- norm{2, ‘approximate’, ‘subsample’} | None, optional
如果為 ‘approximate’ 或 ‘subsample’,則視窗會通過最大值進行正規化,並且偶數長度視窗的校正比例因子會使用
M**2/(M**2+NW)(“approximate”)或基於 FFT 的子樣本位移(“subsample”)來應用,請參閱「註解」以了解詳細資訊。如果為 None,則當Kmax=None時使用 “approximate”,否則使用 2(使用 l2 範數)。- return_ratiosbool, optional
如果為 True,則除了視窗外,還會傳回集中度比率。
- 傳回值:
- vndarray,形狀 (Kmax, M) 或 (M,)
DPSS 視窗。如果 Kmax 為 None,則為 1D。
- rndarray,形狀 (Kmax,) 或 float, optional
視窗的集中度比率。僅當 return_ratios 評估為 True 時傳回。如果 Kmax 為 None,則為 0D。
註解
此計算使用 [2] 中給出的三對角線特徵向量公式。
對於
Kmax=None的預設正規化,即視窗產生模式,僅使用 l-infinity 範數會建立具有兩個單位值的視窗,這會在偶數階和奇數階之間產生輕微的正規化差異。對於偶數樣本數,使用M**2/float(M**2+NW)的近似校正來抵消此效應(請參閱下面的範例)。對於非常長的訊號(例如,1e6 個元素),計算數量級較短的視窗並使用內插可能很有用(例如,
scipy.interpolate.interp1d)以獲得長度為 M 的錐度,但通常這不會保留錐度之間的正交性。在 1.1 版本中新增。
參考文獻
[1]Percival DB, Walden WT. Spectral Analysis for Physical Applications: Multitaper and Conventional Univariate Techniques. Cambridge University Press; 1993.
[2]Slepian, D. Prolate spheroidal wave functions, Fourier analysis, and uncertainty V: The discrete case. Bell System Technical Journal, Volume 57 (1978), 1371430.
[3]Kaiser, JF, Schafer RW. On the Use of the I0-Sinh Window for Spectrum Analysis. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. ASSP-28 (1): 105-107; 1980.
範例
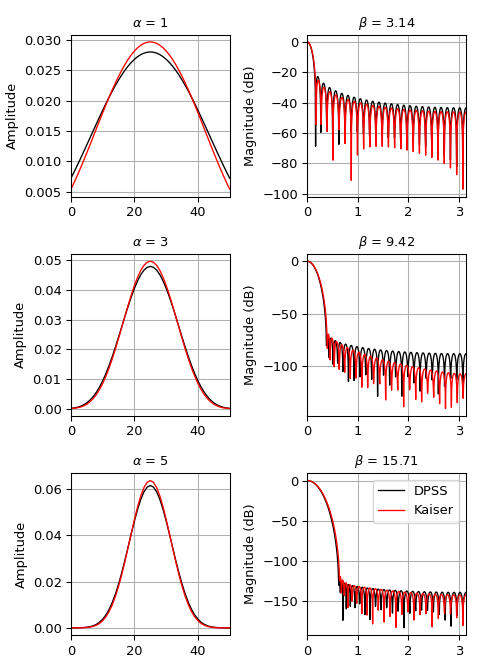
我們可以將此視窗與
kaiser進行比較,後者被發明作為更容易計算的替代方案 [3](範例改編自 此處)>>> import numpy as np >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> from scipy.signal import windows, freqz >>> M = 51 >>> fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, 2, figsize=(5, 7)) >>> for ai, alpha in enumerate((1, 3, 5)): ... win_dpss = windows.dpss(M, alpha) ... beta = alpha*np.pi ... win_kaiser = windows.kaiser(M, beta) ... for win, c in ((win_dpss, 'k'), (win_kaiser, 'r')): ... win /= win.sum() ... axes[ai, 0].plot(win, color=c, lw=1.) ... axes[ai, 0].set(xlim=[0, M-1], title=r'$\alpha$ = %s' % alpha, ... ylabel='Amplitude') ... w, h = freqz(win) ... axes[ai, 1].plot(w, 20 * np.log10(np.abs(h)), color=c, lw=1.) ... axes[ai, 1].set(xlim=[0, np.pi], ... title=r'$\beta$ = %0.2f' % beta, ... ylabel='Magnitude (dB)') >>> for ax in axes.ravel(): ... ax.grid(True) >>> axes[2, 1].legend(['DPSS', 'Kaiser']) >>> fig.tight_layout() >>> plt.show()
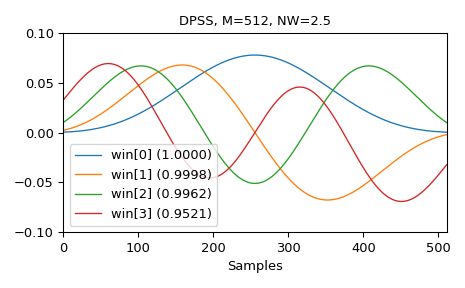
以下是前四個視窗的範例,以及它們的集中度比率
>>> M = 512 >>> NW = 2.5 >>> win, eigvals = windows.dpss(M, NW, 4, return_ratios=True) >>> fig, ax = plt.subplots(1) >>> ax.plot(win.T, linewidth=1.) >>> ax.set(xlim=[0, M-1], ylim=[-0.1, 0.1], xlabel='Samples', ... title='DPSS, M=%d, NW=%0.1f' % (M, NW)) >>> ax.legend(['win[%d] (%0.4f)' % (ii, ratio) ... for ii, ratio in enumerate(eigvals)]) >>> fig.tight_layout() >>> plt.show()
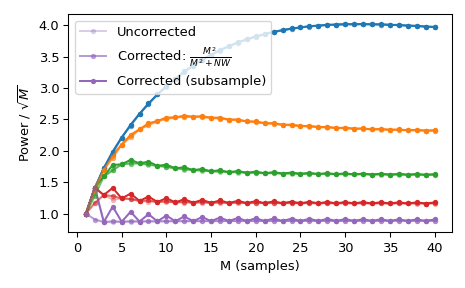
使用標準 \(l_{\infty}\) 範數會為偶數 M 產生兩個單位值,但僅為奇數 M 產生一個單位值。這會產生不均勻的視窗功率,可以通過近似校正
M**2/float(M**2+NW)來抵消,可以通過使用norm='approximate'來選擇(這與Kmax=None時的norm=None相同,此處就是這種情況)。或者,可以使用較慢的norm='subsample',它使用頻域 (FFT) 中的子樣本位移來計算校正>>> Ms = np.arange(1, 41) >>> factors = (50, 20, 10, 5, 2.0001) >>> energy = np.empty((3, len(Ms), len(factors))) >>> for mi, M in enumerate(Ms): ... for fi, factor in enumerate(factors): ... NW = M / float(factor) ... # Corrected using empirical approximation (default) ... win = windows.dpss(M, NW) ... energy[0, mi, fi] = np.sum(win ** 2) / np.sqrt(M) ... # Corrected using subsample shifting ... win = windows.dpss(M, NW, norm='subsample') ... energy[1, mi, fi] = np.sum(win ** 2) / np.sqrt(M) ... # Uncorrected (using l-infinity norm) ... win /= win.max() ... energy[2, mi, fi] = np.sum(win ** 2) / np.sqrt(M) >>> fig, ax = plt.subplots(1) >>> hs = ax.plot(Ms, energy[2], '-o', markersize=4, ... markeredgecolor='none') >>> leg = [hs[-1]] >>> for hi, hh in enumerate(hs): ... h1 = ax.plot(Ms, energy[0, :, hi], '-o', markersize=4, ... color=hh.get_color(), markeredgecolor='none', ... alpha=0.66) ... h2 = ax.plot(Ms, energy[1, :, hi], '-o', markersize=4, ... color=hh.get_color(), markeredgecolor='none', ... alpha=0.33) ... if hi == len(hs) - 1: ... leg.insert(0, h1[0]) ... leg.insert(0, h2[0]) >>> ax.set(xlabel='M (samples)', ylabel=r'Power / $\sqrt{M}$') >>> ax.legend(leg, ['Uncorrected', r'Corrected: $\frac{M^2}{M^2+NW}$', ... 'Corrected (subsample)']) >>> fig.tight_layout()